2025. 3. 31. 06:50ㆍWonderful World
Tepui (or Tepuy) Mountains : Auyantepui, Autana, Neblina, and Mount Roraima.
in
Venezuela, Brazil, Guyana, Suriname

Tepui (or Tepuy) Mountains

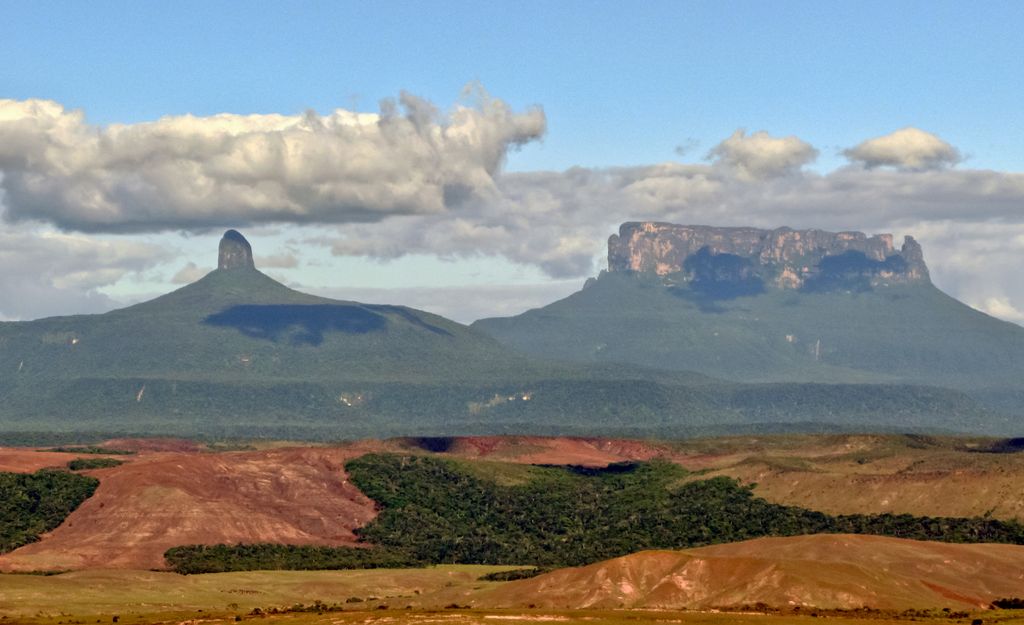
Eastern tepuis chain - Gran Sabana

Ecoregion territory (in purple)
Geography
Area : 50,675 km2 (19,566 sq mi)
Countries : Venezuela Brazil Guyana Suriname

A tepui /ˈtɛpwi/, or tepuy (Spanish: [teˈpuj]), is a table-top mountain or mesa found in South America, especially in Venezuela and western Guyana. The word tepui means "house of the gods" in the native tongue of the Pemon, the indigenous people who inhabit the Gran Sabana.
Tepuis tend to be found as isolated entities rather than in connected ranges, which makes them the host of a unique array of endemic plant and animal species. Notable tepuis include Auyantepui, Autana, Neblina, and Mount Roraima. They are typically composed of sheer blocks of Precambrian quartz arenite sandstone that rise abruptly from the jungle. Auyantepui is the source of Angel Falls, the world's tallest waterfall.

Tramen Massif and Karaurín-tepui
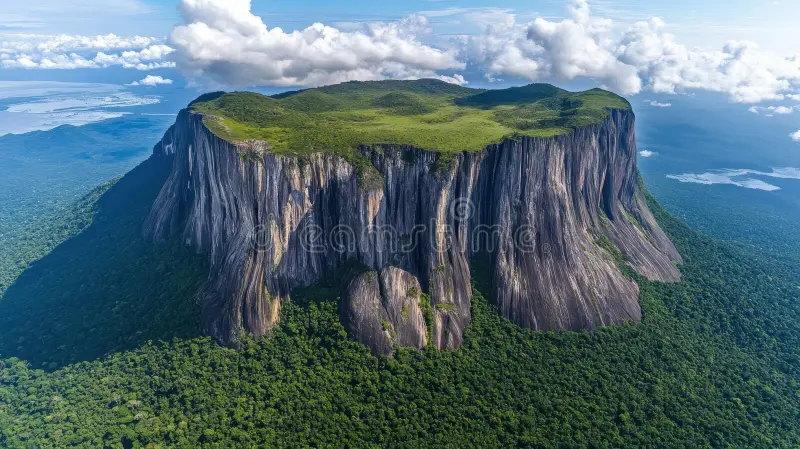


aerial view-tepui formation
showcasing-its steep cliffs-dense vegetation-under cloudy sky
shot-sheer meet-lush beneath
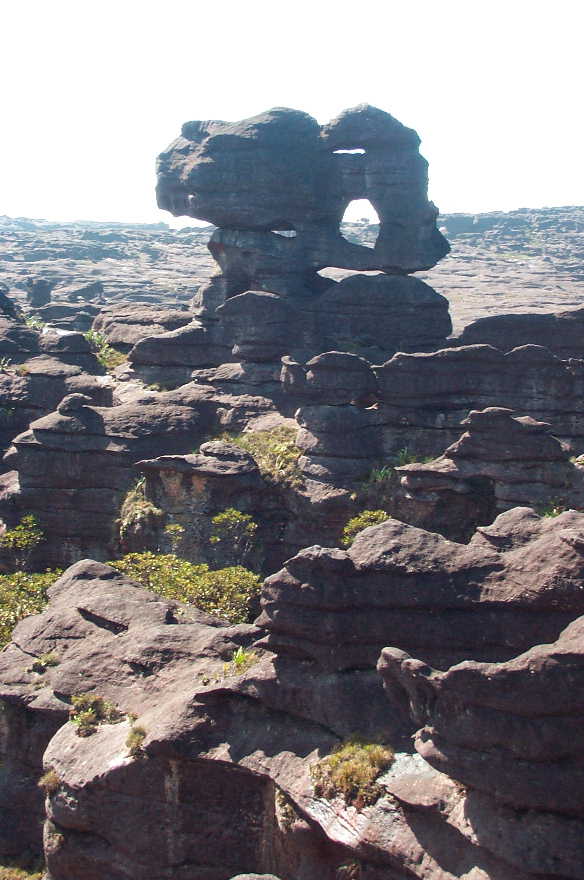

The plateau of Mount Roraima – the peculiar rock formation is caused by erosion.

panoramic-view-gran-sabana-tepuis

Amazon tepui mountain
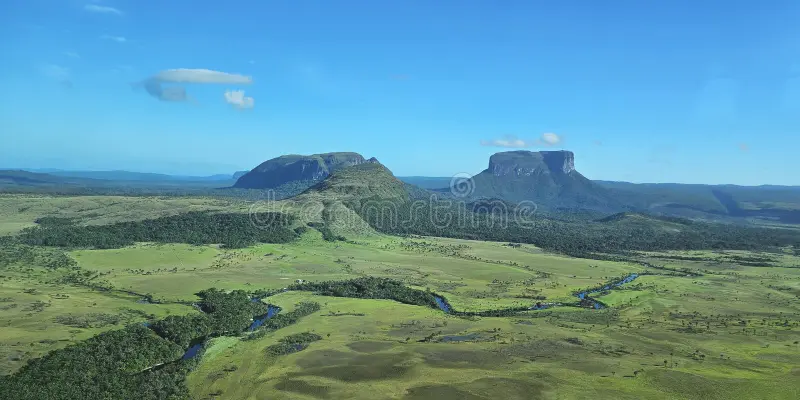

view-tepui venezuela-canaima park
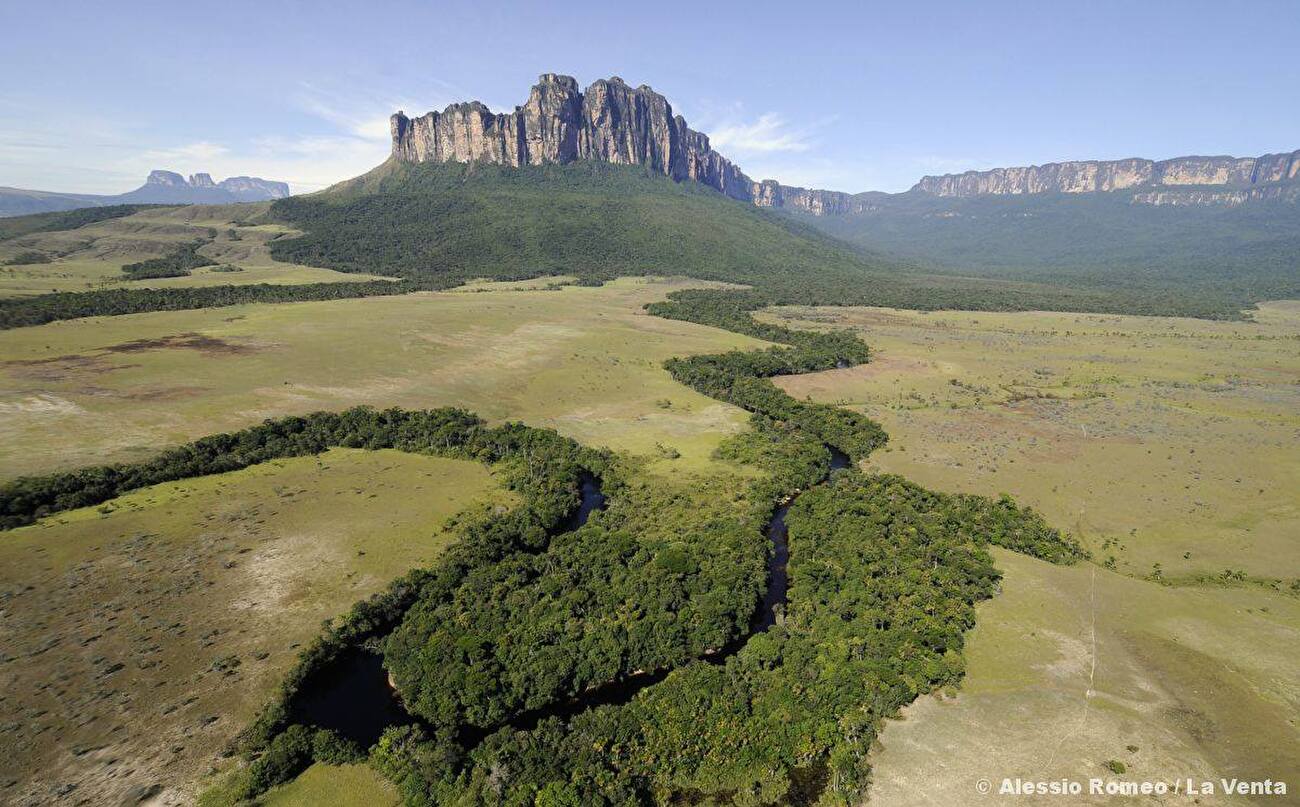

Morphology
* morphology [mɔːrfάlədʒi] 형태학, 형태, 어형론

These table-top mountains are the remains of a large sandstone plateau that once covered the granite basement complex between the north border of the Amazon Basin and the Orinoco, between the Atlantic coast and the Rio Negro. This area is part of the remnants of the supercontinent Gondwana. Throughout the course of the history of Earth, the plateau began to erode and fragment about 300 million years ago, and about 70 million years ago the tepuis were formed from the remaining monadnocks.
There are 115 such mesas in the Gran Sabana in the south-east of Venezuela on the border with Guyana and Brazil, where the highest concentration of tepuis is found. The precipitous mountains tower over the surrounding area by up to 1,000 metres (3,000 ft).
Tepuis range in elevation from 1,000–3,000 metres (3,000–10,000 ft). The total surface area of all 115 tepuis is approximately 5,000 km2 (2,000 sq mi).
Because of their great age, some tepuis exhibit surface features and caves typical of karst topography, formed in more water-soluble rocks such as limestone. Caves here include the 671-metre-deep (2,201 ft) Abismo Guy Collet, the deepest quartzite cave in the world. Some of the mesas are pocked with giant sinkholes up to 300 meters (1,000 ft) in diameter and with sheer walls up to 300 meters (1,000 ft) deep. These sinkholes are formed when the roofs of tunnels carved by underground rivers collapse.

panoramic-view-gran-sabana-tepuis
Auyantepui

Auyán-tepui (Spanish pronunciation: [awˈʝan teˈpuj]), also spelled Ayan, is a tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. It is the most visited and one of the largest (but not the highest) tepuis in the Guiana Highlands, with a summit area of 666.9 km2 (257.5 sq mi) and an estimated slope area of 715 km2 (276 sq mi).
The unevenly heart-shaped summit plateau of Auyán-tepui is heavily inclined, rising from around 1,600 metres (5,200 ft) in the northwest to a maximum of 2,450 m (8,040 ft) in the southeast. It is incised from the north by a vast valley, the Cañón del Diablo (Devil's Canyon), formed by the Churún River. The larger western portion of the plateau is partially forested, whereas the eastern part comprises mostly bare rock with only patchy vegetation cover. The mountain hosts a number of extensive cave systems.
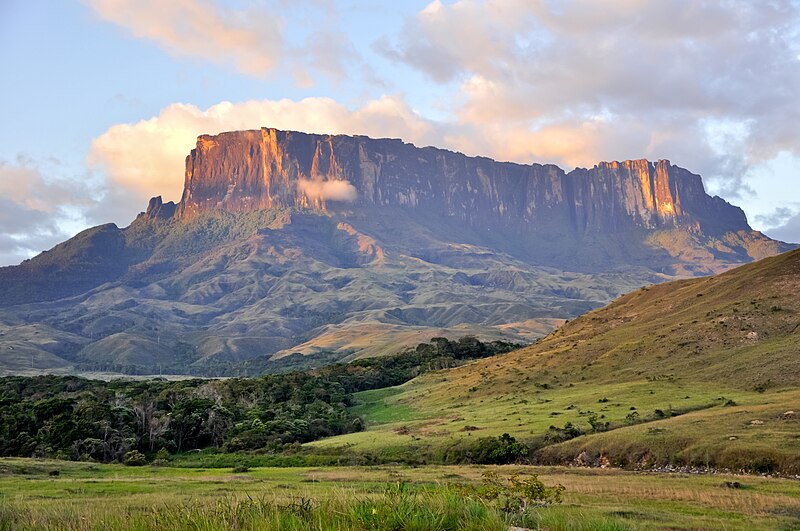

Kukenan Tepuy Sunset
Kukenan Tepuy in Gran Sabana National Park, Venezuela. Photo taken from Tëk River Camp at 5:20 p.m. Tepuy height: 2700-2800 mts.
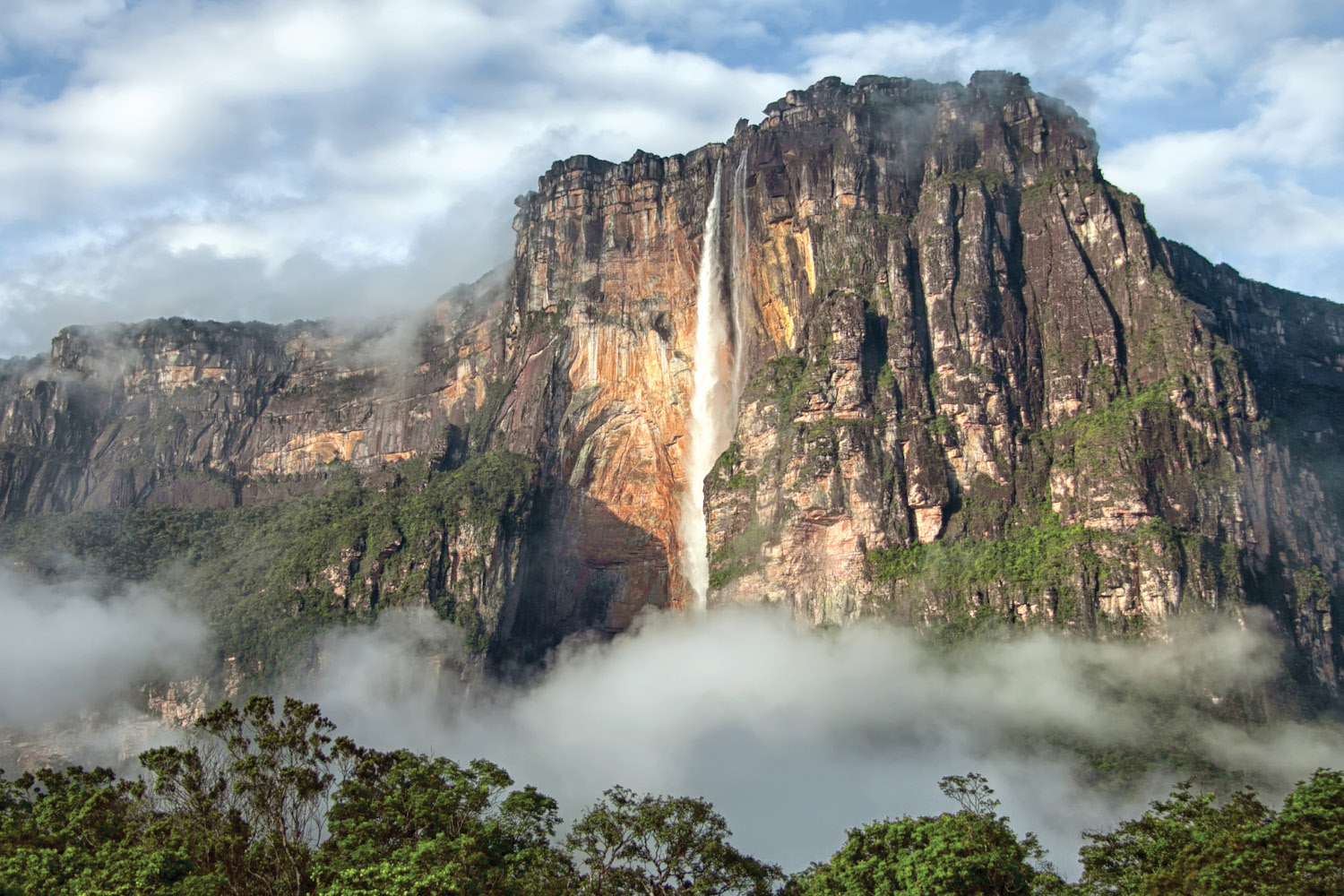

Angel Falls (Spanish: Salto Ángel; Pemon: Kerepakupai Merú or Parakupá Vená) is a waterfall in Venezuela. It is the world's tallest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 metres (3,212 ft), and a plunge of 807 m (2,648 ft).
The waterfall drops over the edge of the Auyán-tepui mountain in the Canaima National Park (Spanish: Parque Nacional Canaima), a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Gran Sabana region of Bolívar State. The height figure, 979 m (3,212 ft), mostly consists of the main plunge but also includes about 400 metres (1,300 ft) of sloped cascade and rapids below the drop and a 30-metre-high (100 ft) plunge downstream of the talus rapids.

Angel_falls_panorama
Partly clouded view of Auyán-tepui and Angel Falls (centre) from Isla Raton camp, taken during the end of the dry season
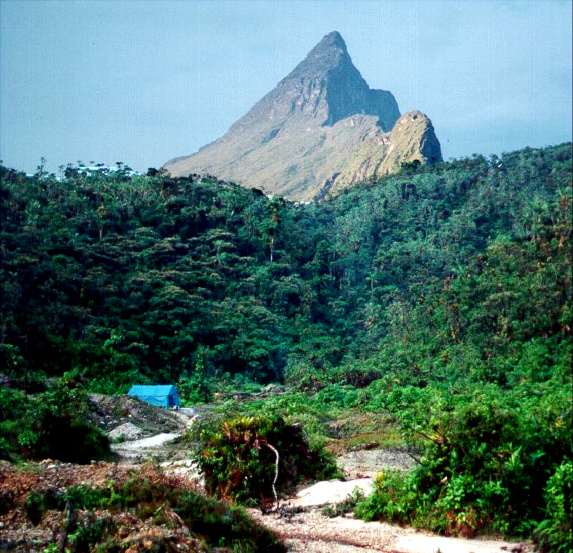
Autana
"Autana" can refer to several things, including a mountain (tepui) in Venezuela, a river in the middle Orinoco basin, a municipality in Amazonas state, a genus of cellar spiders, a monotypic genus of flowering plants, and a model of Toyota Land Cruiser.
Cerro Autana (Autana Mountain) is a geological formation located at the western portion of the Guiana Shield in the Estado Amazonas, Venezuela near the Colombian border. It is characterized by a narrow base, a flat top, and almost vertical walls. Its top is at approximately 1,220 metres (4,000 ft). It belongs to the formations known as tepuis which are characteristic flat-top mountains of the Guiana Shield. Cerro Autana (Wahari-Kuawai ) plays the role of the "tree of life" in the oral history and lore of the Piaroa Indians who inhabit the region.
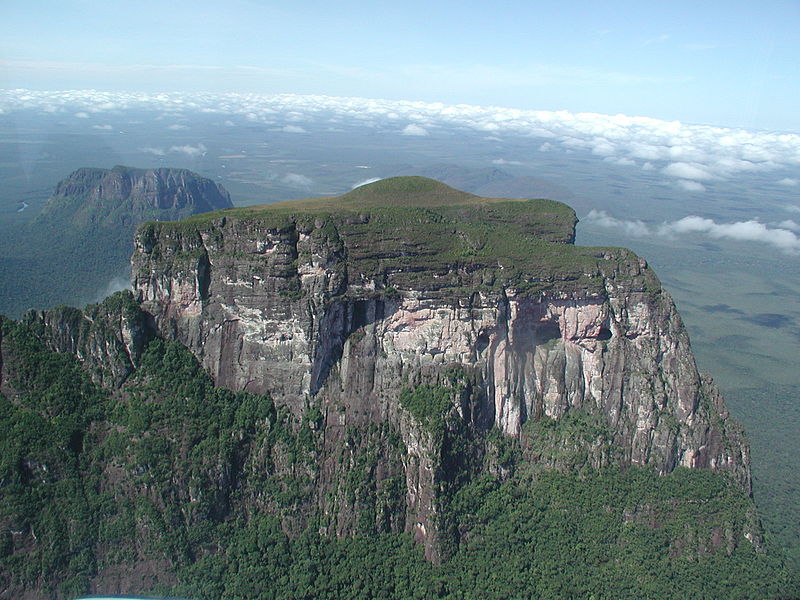

Cerro Autana. Northern exposure. The entrances to the caves are seen on the right side below the line of vegetation.

Steve Platt on North Ridge, Autana 1974
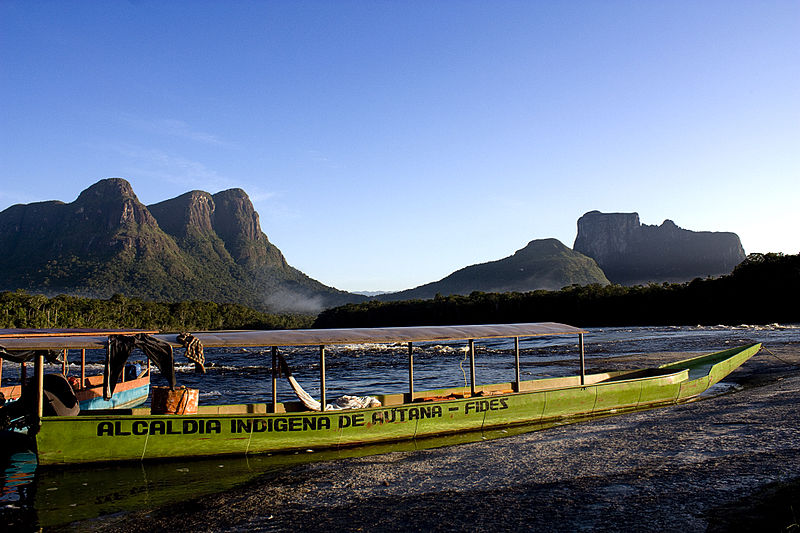

Cerro Autana in Amazonas state, Venezuela.
Neblina
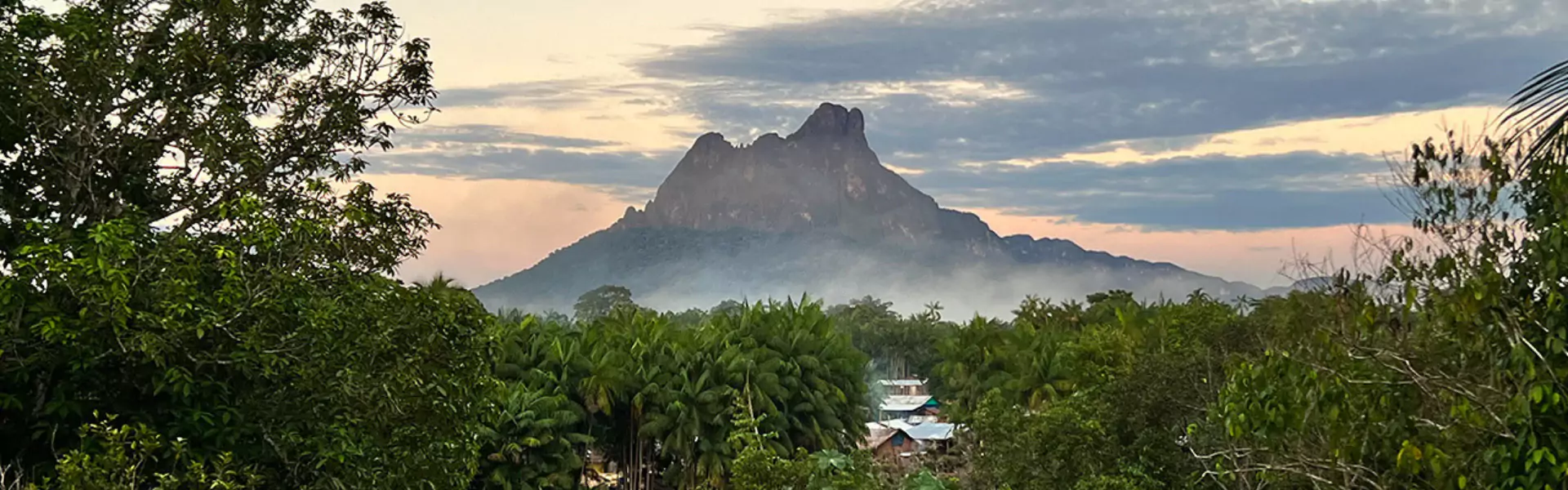

Pico da Neblina-Nacional Parque
Cerro de la Neblina - Wikipedia
Cerro de la Neblina (lit. "Mountain of the Mist"[2]), also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil[3] and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela,[4] is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep cany
en.wikipedia.org
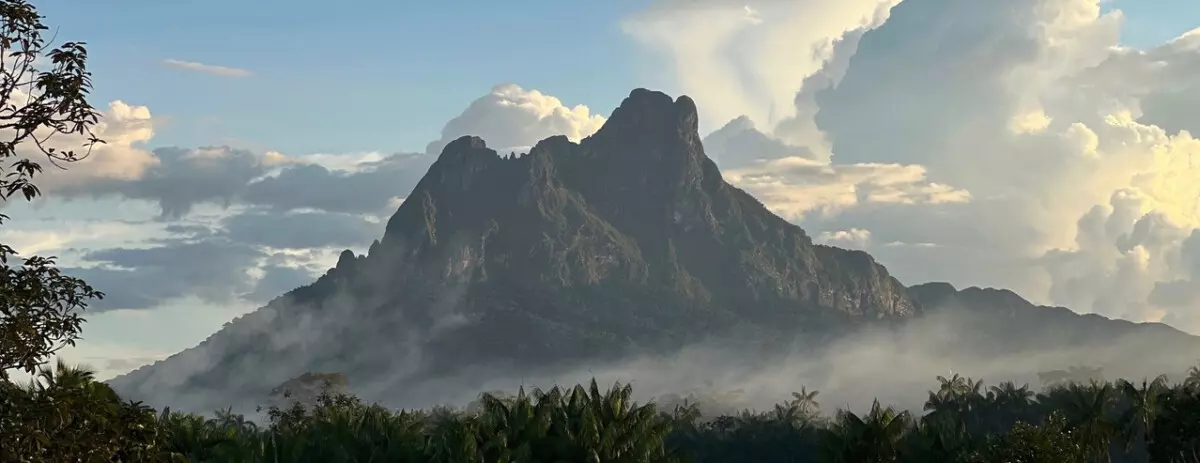

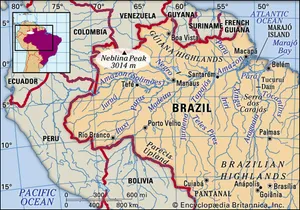

Neblina Peak, peak in the Imeri Mountains, Amazonas estado (state), northern Brazil, near the Venezuelan border. Reaching 9,888 feet (3,014 metres) above sea level, it is the highest point in Brazil. Until Neblina was discovered in 1962, Bandeira Peak was thought to be Brazil’s highest mountain.

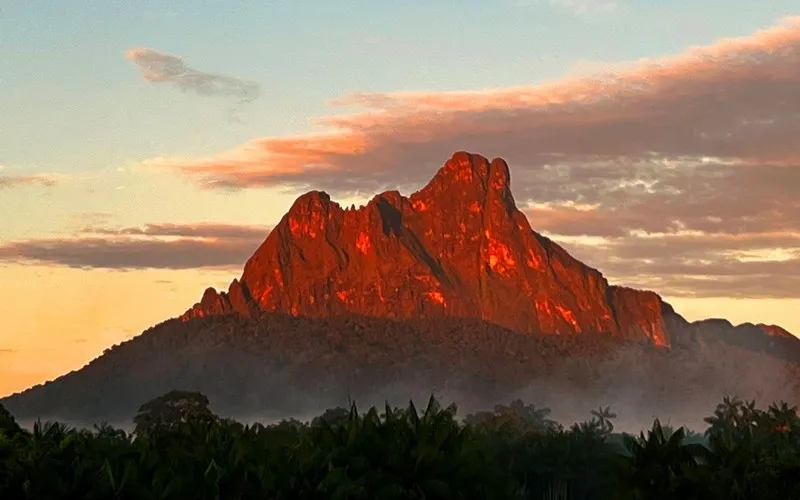
Pico da Neblina in 1998 seen from the distance, without the usual clouds. The round blue-shaded secondary peak just behind it is Pico 31 de Março.
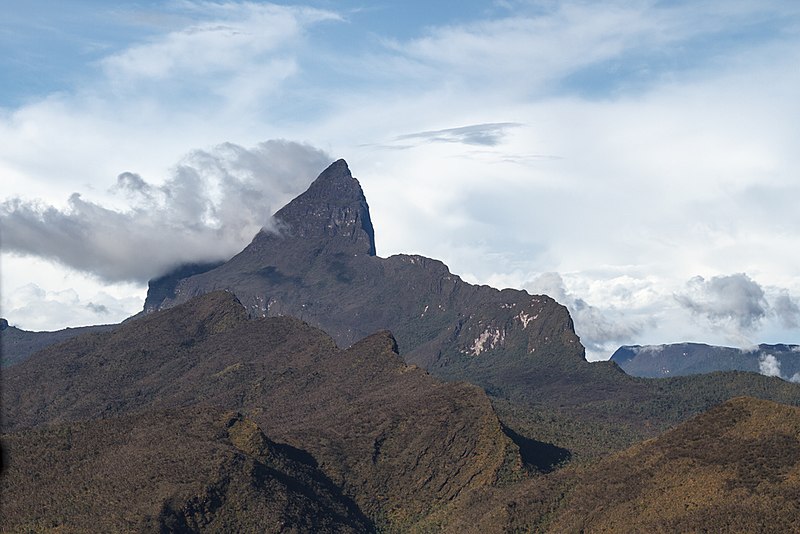

Pico da Neblina (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈpiku dɐ neˈblĩnɐ], Mist Peak) is the highest peak in Brazil, 2,995.3 metres (9,827 ft) above sea level, in the Serra da Neblina, part of the Serra do Imeri, a section of the Guiana Highlands on the Brazil-Venezuela border. As determined by a border survey expedition in 1962, its summit lies just within Brazilian territory, at a horizontal distance of only 687 m (2,254 ft) from the Venezuelan border at Pico 31 de Março. It is a common misconception to refer to this mountain as the highest point in South America outside the Andes while ignoring the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in Colombia.
As the peak's name suggests, it is shrouded in dense clouds most of the time. It was first ascended in 1965 by members of a Brazilian Army expedition.
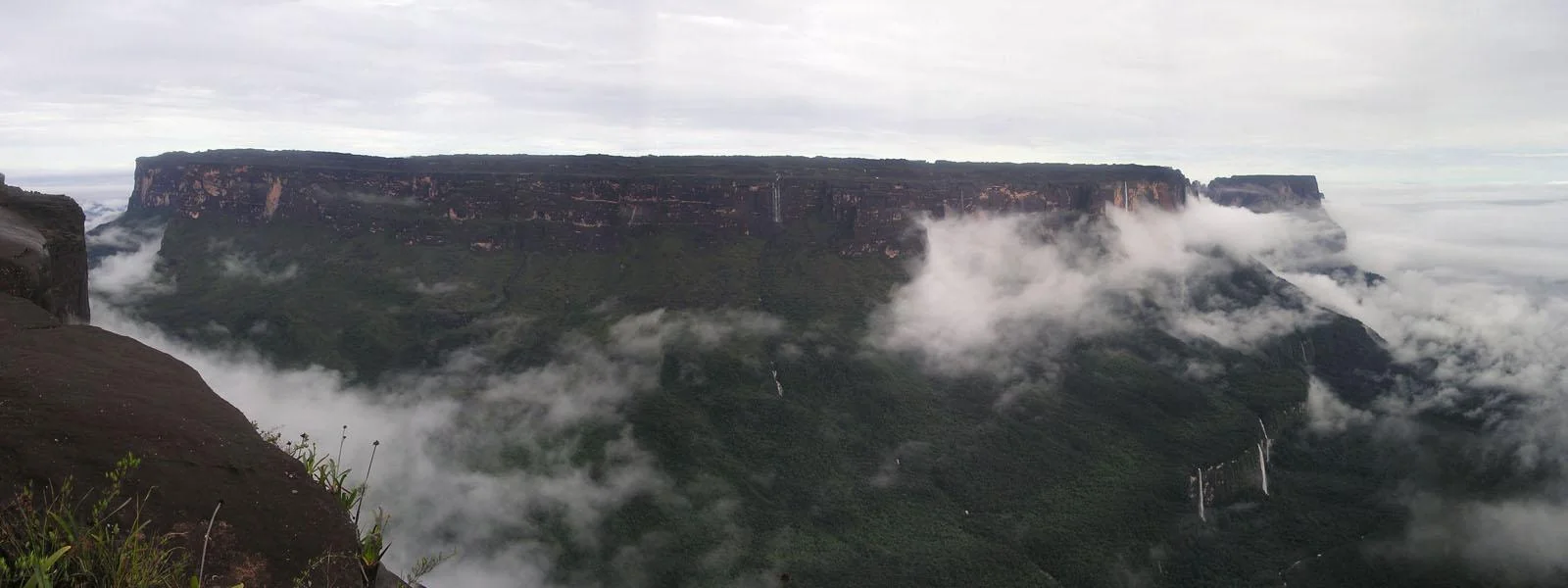
Mount Roraima
Mount Roraima - Wikipedia
Mountain in Brazil, Guyana and Venezuela Mount Roraima (Spanish: Monte Roraima; Tepuy Roraima; Cerro Roraima; Portuguese: Monte Roraima) is the highest of the Pacaraima chain of tepuis (table-top mountain) or plateaux in South America.[4]: 156 [c] It i
en.wikipedia.org
Mount Roraima (Spanish: Monte Roraima; Tepuy Roraima; Cerro Roraima; Portuguese: Monte Roraima) is the highest of the Pacaraima chain of tepuis (table-top mountain) or plateaux in South America. It is located at the junction of Brazil, Guyana and Venezuela.
A characteristic large flat-topped mountain surrounded by cliffs 400–1,000 m (1,300–3,300 ft) high. The highest point of Mount Roraima is located on the southern edge of the cliff at an elevation of 2,810 m (9,220 ft) in Venezuela, and another protrusion at an elevation of 2,772 m (9,094 ft) at the junction of the three countries in the north of the plateau is the highest point in Guyana. The name Mount Roraima came from the native Pemon people. Roroi in the Pemon language means "blue-green", and ma means "great".
Leaching caused by intense rainfall has shaped the peculiar topography of the summit, and the geographical isolation of Mount Roraima has made it home to much endemic flora and fauna.
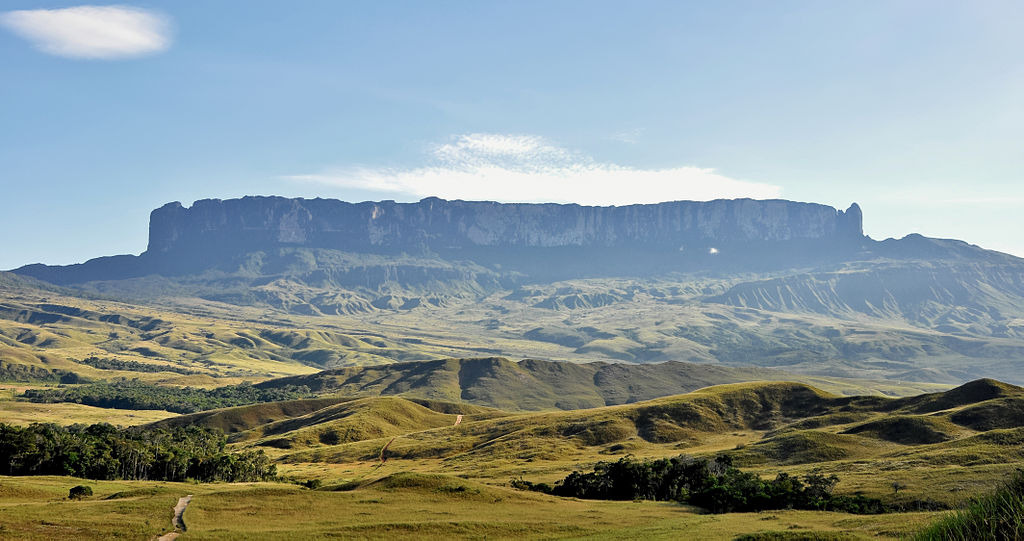

Mount Roraima ( 2,810 m) as seen from the Venezuelan side
Clear morning at Mount Roraima, as seen from the road leading there from Paraitepuy pemon community, in Gran Sabana Venezuela.
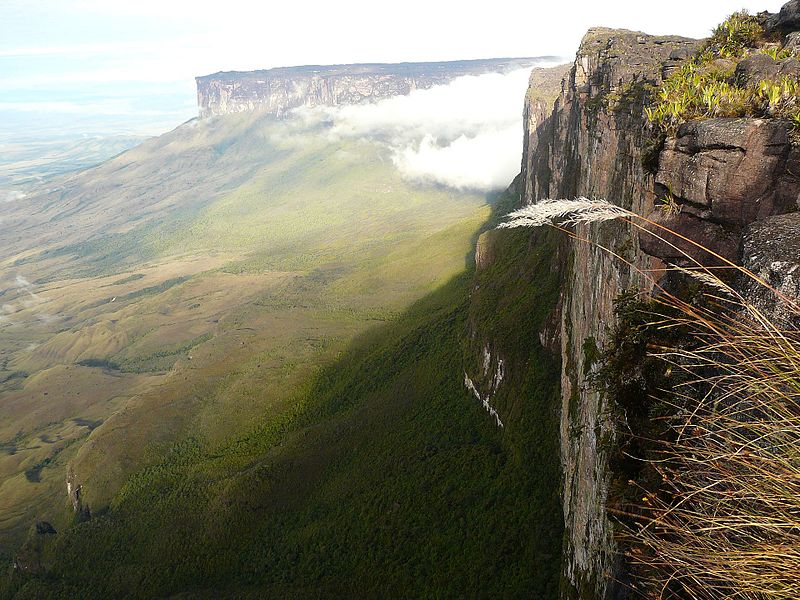

The cliffs of Mount Roraima

Triple Point,_Mount Roraima
Tripoint marker where the borders of Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela meet on top of Mount Roraima
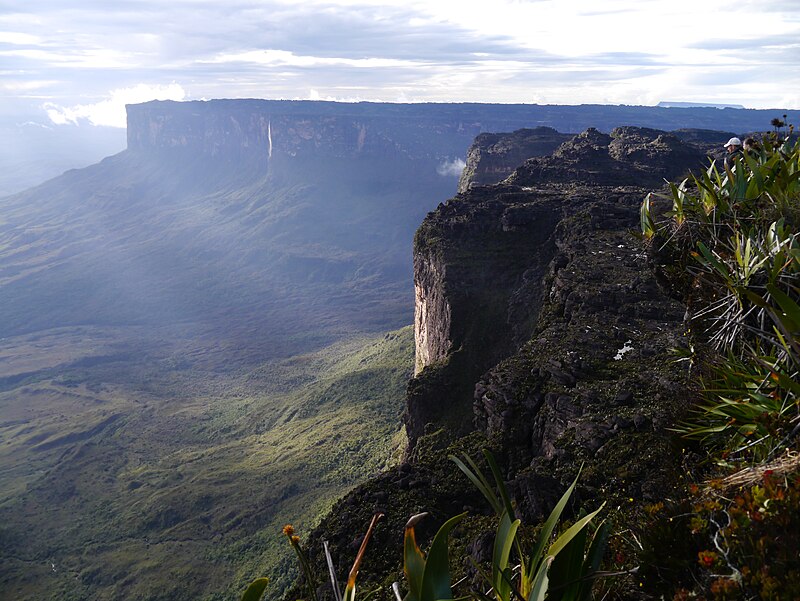

The Roraima Falls, Venezuela
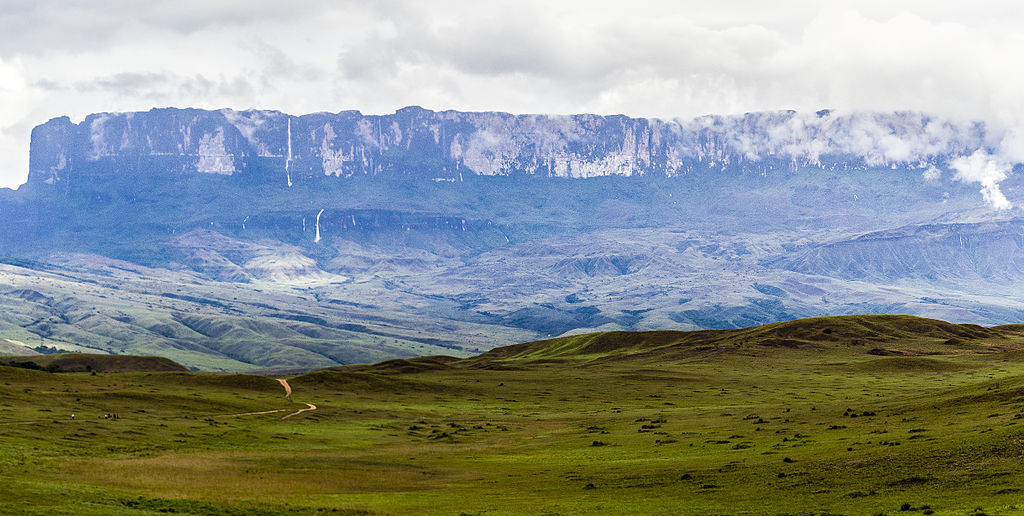

Panorámica _ del_Tepuy Roraima
Mount Roraima and the falls as seen from the Venezuela side
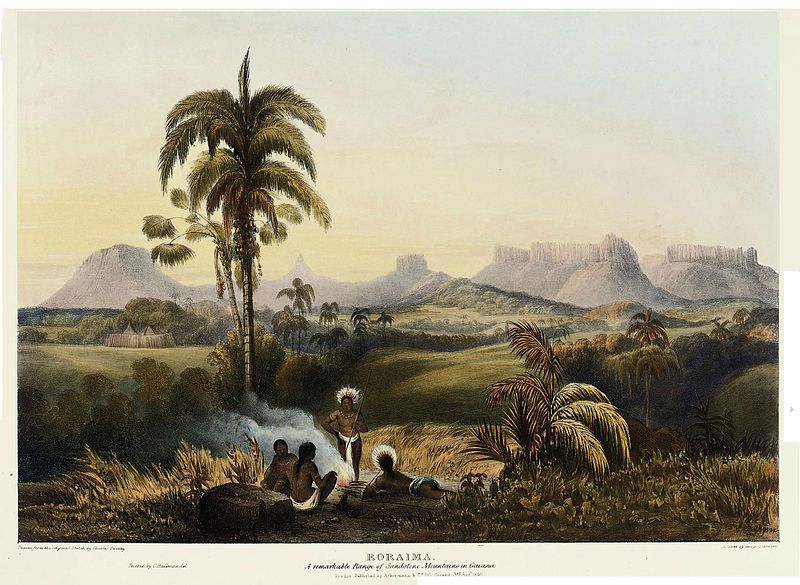

Roraima, A Remarkable Range of Sandstone Mountains in Guiana. Painters Charles Bentley and Robert H. Schomburgk, engraver George Barnard. Published by Ackermann, 1840
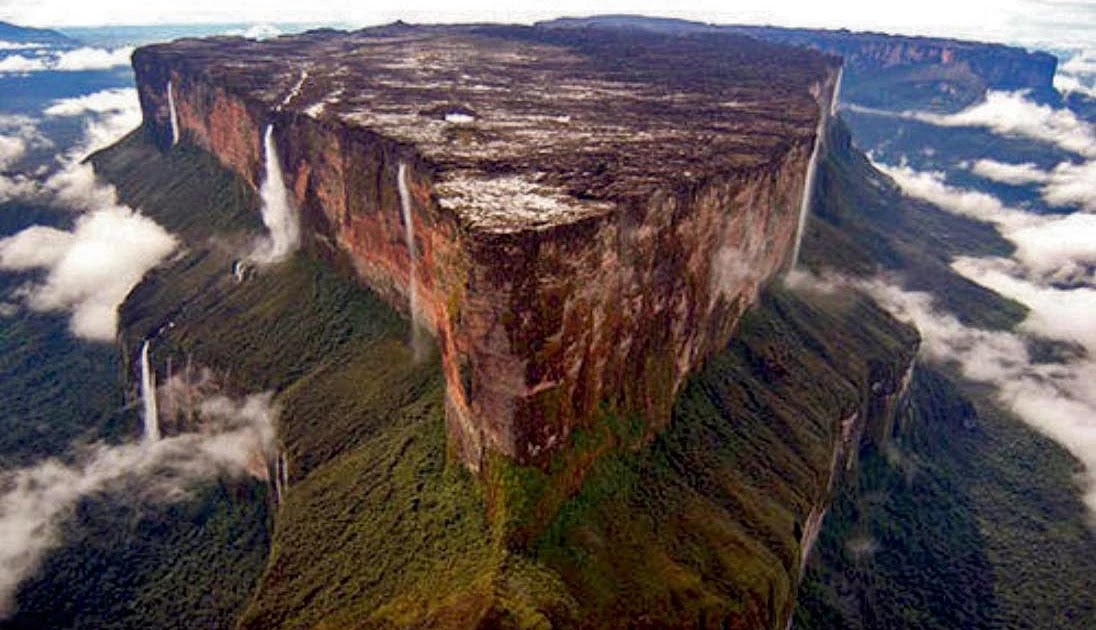

Monte Roraima: Table Top Mountain
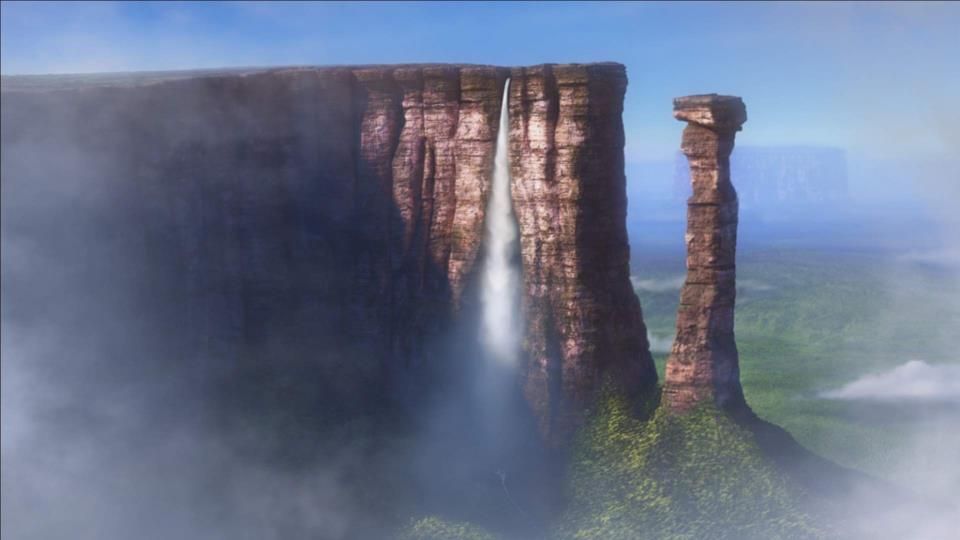

Mount Roraima or Roraima Tepui

Tepui (or Tepuy) Mountains











*****
'Wonderful World' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Moon Valley and Welwitschia, Swakopmund, Namibia (0) | 2025.03.31 |
|---|---|
| NAMIB-NAUKLUFT NATIONAL PARK – NAMIBIA (0) | 2025.03.31 |
| Earth’s Last Untouched Paradises 2 (0) | 2025.03.31 |
| Earth’s Last Untouched Paradises 1 (0) | 2025.03.30 |
| 가야산 국립공원 (0) | 2025.03.30 |